HDPE vs. PVC vs. Steel Conduit: Which Fits Your Electrical Project?
Categories:PVC Pipe and Fitting Author: author
When it comes to electrical installations, conduits are more than protective tubes - they're part of a system that ensures safety, reliability, and long-term performance.
From underground telecom lines to industrial power networks, the material you choose - HDPE, PVC, or Steel - can significantly impact your project's cost, safety, and maintenance.
Let's dive deeper into how each conduit type performs, where it fits best.
HDPE Conduit - Flexible Strength Beneath the Surface
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) conduit has become the preferred choice for underground and directional boring applications.
Its flexibility, chemical resistance, and seamless jointing methods make it perfect for buried installations where terrain shifts or vibration can damage rigid materials.
Advantages of HDPE Conduit
● Long continuous runs - supplied in coils, minimizing the need for couplers
● Excellent resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and soil acidity
● High impact strength - resists crushing even under heavy loads
● UV stability (especially black HDPE) for outdoor use
● Fusion welding or electrofusion joints ensure a watertight system
Typical Applications
● Underground power distribution
● Fiber optic and telecommunication ducts
● Renewable energy farms (solar and wind power cabling)
● Water treatment facilities and irrigation systems
Limitations
● Not suitable for exposed installations needing rigid support
● Requires specialized tools for heat fusion joining
● Non-conductive, so grounding must be handled separately
For projects demanding flexibility and environmental resistance, HDPE conduit stands out as the smart, long-term investment.
PVC Conduit – Simple, Cost-Effective, and Widely Used
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) conduit has long been a staple in electrical infrastructure.
Its combination of affordability, easy installation, and reliable insulation makes it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications where conditions are moderate.
Advantages of PVC Conduit
● Low material and installation cost - easy to cut and solvent-weld
● Corrosion and moisture resistant - suitable for damp or chemical-prone areas
● Lightweight - reduces handling and transport effort
● Non-conductive - eliminates risk of electrical faults through the conduit
● Wide range of fittings and accessories available globally
Applications
● Residential and commercial wiring
● Control panels and building service conduits
● Ceiling and wall-mounted cable systems
● Underground ducts in low-impact zones
Limitations
● Becomes brittle under freezing temperatures
● Lower mechanical strength than steel
● Sensitive to direct sunlight over time (unless UV-stabilized)
PVC conduit shines in cost-sensitive or standard environments where flexibility and ruggedness are less critical but insulation and corrosion resistance are important.
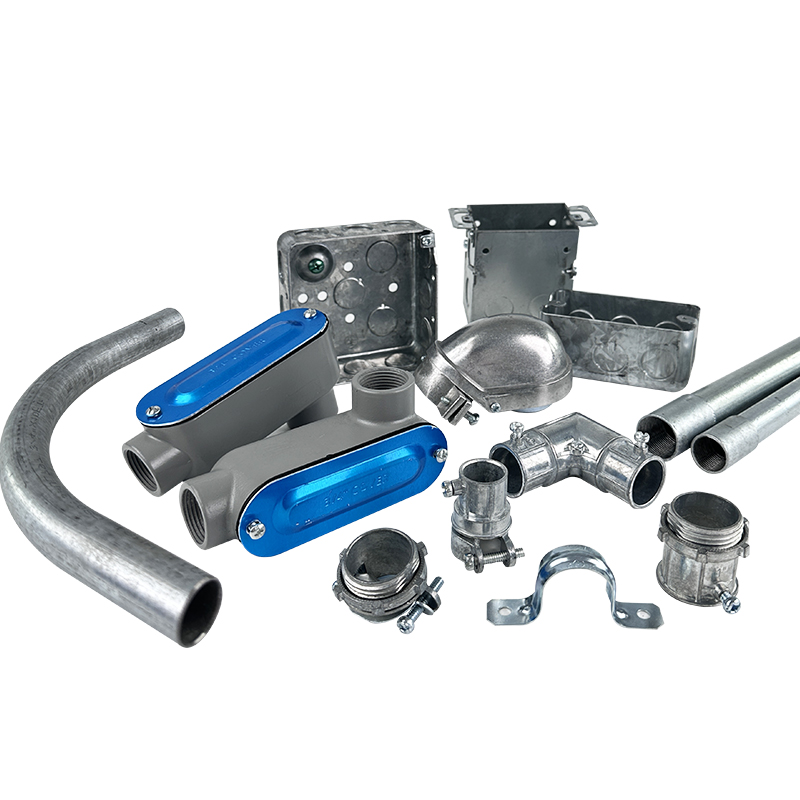
Steel Conduit – The Industrial Powerhouse
If your installation demands mechanical protection, fire resistance, and grounding, Steel conduit is the premium choice.
It has remained the standard for decades in industrial plants, data centers, and high-risk zones.
EMT IMC Electrical Conduit and Fitting
Advantages of Steel Conduit
● Maximum mechanical protection - resists impact and crushing
● Fire-resistant - maintains integrity under high temperature
● Provides natural grounding and EMI shielding
● Excellent longevity with proper galvanizing or coating
● Professional appearance in exposed environments
Applications
● Industrial plants, oil & gas facilities
● Transportation infrastructure (tunnels, stations)
● Data centers and commercial electrical rooms
● Outdoor and rooftop installations
Limitations
● Heavier than plastic conduits, requiring more labor
● Needs threading, bending tools, and skilled workers
● Prone to corrosion without protective coatings
● Higher upfront cost, though offset by longevity
Steel conduits are ideal when safety and durability outweigh initial cost - especially in environments exposed to physical stress or heat.
How to Choose: Quick Comparison
|
Feature |
HDPE Conduit |
PVC Conduit |
Steel Conduit |
|
Flexibility |
Excellent – coiled lengths |
Limited – needs elbows |
Rigid – needs bending |
|
Mechanical Strength |
Moderate |
Fair |
Excellent |
|
Fire Resistance |
Low |
Moderate |
High |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Excellent |
Good |
Coated required |
|
UV Resistance |
High (black HDPE) |
Moderate |
High |
|
Weight |
Light |
Light |
Heavy |
|
Electrical Conductivity |
Non-conductive |
Non-conductive |
Conductive |
|
Cost Level |
Medium |
Low |
High |
|
Installation Speed |
Fast with fusion |
Easy, manual |
Slower, labor-intensive |
How to Select Electrical Conduits for Your Project?
When you sit down to pick which conduit to use, think through these questions:
What is the environment? (Indoor/outdoor, buried/exposed, chemical exposure, temperature extremes)
What is the mechanical risk? (Will it be in a traffic zone, subject to impacts, overhead installation?)
How complex is the routing? (Lots of bends, obstacles, need for long continuous runs?)
What is the budget, and what about long-term maintenance?
Do you need the conduit to act as grounding/shielding, or is non-metallic acceptable?
Are local codes, fire-rating, temperature rating, installation method requirements driving your choice?
What about installation labour, joint count, time to install?
Are there future-proofing or swapping of cables expected (i.e., does conduit need to be accessible)?
Based on the answers:
● If you have a long underground route with few bends → HDPE may be best.
● If you have a standard building interior project and cost is key → PVC is a smart choice.
● If the environment is harsh, exposed, high mechanical stress or needing fire rating → steel conduit likely fits.
Practical Selection Guide
Every project faces unique site conditions. Here's how to align conduit material with your needs:
1. Underground Utility Projects
HDPE is unbeatable for long-distance or curved routing. It withstands soil pressure and resists water infiltration.
PVC can also be used, but requires more joints and elbows, increasing maintenance risk.
2. Industrial and High-Temperature Environments
Steel conduit's rigidity, grounding ability, and fire tolerance make it the safest bet for hazardous sites and factory floors.
3. Commercial and Residential Buildings
PVC conduit is a cost-friendly choice for concealed wiring and general construction. Its ease of cutting and joining saves labor time.
4. Marine, Mining, or Outdoor Projects
HDPE offers superior corrosion resistance to saltwater and chemicals, making it ideal for coastal or underground utility work.
5. Hybrid Systems
In large projects, engineers often combine materials - HDPE underground, PVC indoors, and Steel in exposed mechanical rooms - to balance performance and cost.
Electrical Conduit Manufacturer and Supplier
Conclusion
Each conduit material - HDPE, PVC, and Steel - has unique strengths. The best choice depends on your project's environment, budget, safety standards, and installation needs.
● HDPE conduit provides unmatched flexibility and corrosion resistance for underground and curved runs.
● PVC conduit is practical, affordable, and ideal for general electrical installations.
● Steel conduit offers superior durability, grounding, and fire safety in demanding conditions.
No matter what your specification requires, ULP delivers all three - backed by OEM/ODM customization, quality assurance, and one-stop service. From design consultation to final delivery, ULP helps you build conduit systems that last.
If your next electrical project involves HDPE, PVC, or Steel conduits, contact ULP to get expert advice and a tailored solution for your specific environment.